Learn
Kidney Care
Learn what common causes of Kidney Failure are and what signs may occur when identifying the disease.
Know the basics
The Kidneys Functions
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a condition characterized by a gradual loss of kidney function over time. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, which are then excreted in urine. When kidney function declines, waste accumulates in the body, leading to various health issues.
Blood Pressure
Healthy kidney’s help to regulate your blood pressure.
Chemical Balance
Help maintain chemical balance and fluid balance of the body.
Excess Waste
Kidneys help expel excess waste & fluids from the body.
Red Blood Cells
The kidneys notify the body when red blood cells are needed.
National Kidney Foundation. (2024, January 15). What is kidney disease? | The kidney disease, heart disease, and diabetes connection [Video]. YouTube.
Know the basics
Causes of CKD
Several Factors Can Lead to the Development of CKD, including:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Increased pressure can harm kidney tissues.
- Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the kidney's filtering units.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease: A genetic disorder causing cysts in the kidneys.
- Prolonged Obstruction: Conditions like kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can block urine flow, leading to damage.
What to Watch For
Symptoms of CKD
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) progresses silently in its early stages, often showing no obvious symptoms until kidney function is significantly impaired. As the disease advances, a range of physical and systemic symptoms may develop. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for managing CKD and slowing its progression.
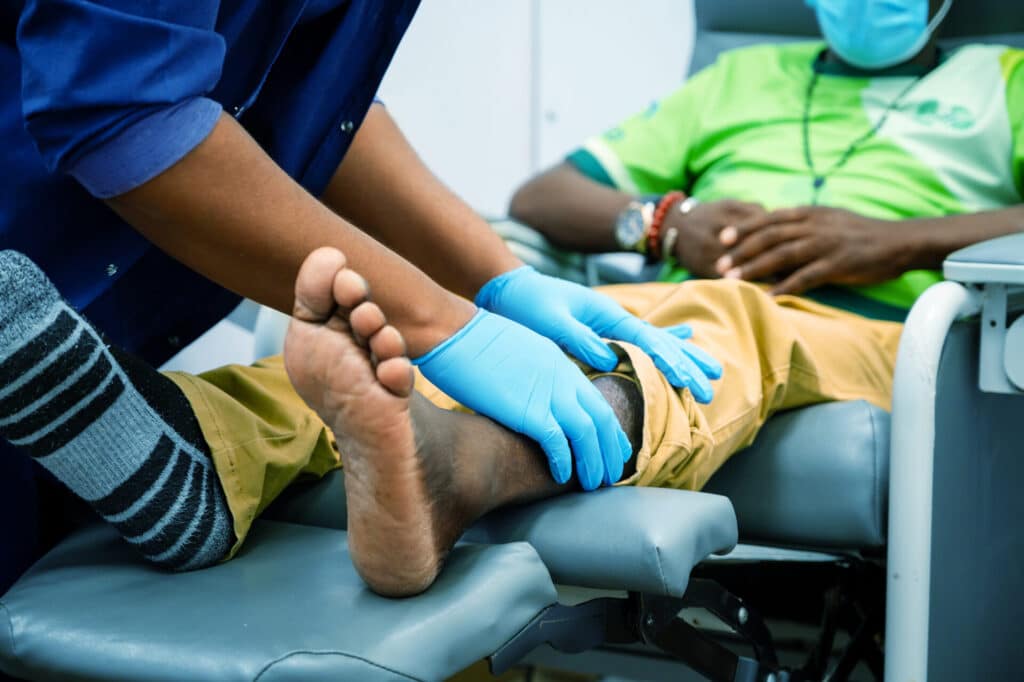
Early Signs & Mild Symptoms
In the initial phases, CKD may not cause noticeable discomfort. However, subtle changes can indicate kidney stress, including:
- Fatigue & Low Energy – A general feeling of weakness due to toxin buildup in the blood.
- Changes in Urination – Frequent nighttime urination (nocturia), foamy urine, or reduced output.
- Loss of Appetite & Nausea – A result of waste accumulation in the body, affecting digestion.
- Mild Swelling (Edema) – Puffiness in the ankles or hands due to fluid retention.
- Dry & Itchy Skin –Caused by mineral imbalances and toxin accumulation.
What to Watch For
Advanced CKD Symptoms
As kidney function declines, waste and fluid buildup in the body can lead to more serious symptoms.
Severe Fluid Retention & Swelling
- Noticeable swelling in the legs, feet, face, and hands due to fluid imbalances.
- Shortness of breath caused by fluid buildup in the lungs (pulmonary edema).
Blood & Toxin Imbalances
- High blood pressure (hypertension) – Damaged kidneys struggle to regulate fluids and sodium.
- Anemia & Cold Sensitivity – A decline in red blood cell production, leading to frequent chills and fatigue.
- Dizziness & Brain Fog – Poor kidney function may reduce oxygen levels in the brain, causing concentration issues, confusion, and headaches.
Digestive & Metabolic Issues
- Metallic Taste & Ammonia Breath – Due to uremia (waste buildup) affecting taste and breath odor.
- Muscle Cramps & Weakness – Caused by electrolyte imbalances (low calcium, high potassium, or magnesium deficiency).
Pain & Discomfort
- Flank or Lower Back Pain – Especially in cases of kidney infections, kidney stones, or polycystic kidney disease (PKD).
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) – A common issue in CKD patients, leading to uncontrollable leg movements at night.
When should you see a doctor?
If you experience persistent fatigue, swelling, difficulty breathing, or changes in urination, it’s essential to consult a nephrologist. Routine kidney function tests (such as GFR, creatinine, and urine protein tests) can detect CKD early, helping you manage symptoms before they worsen.
Generally, patients are advised to consult a nephrologist from CKD Stage 3 onward, and dialysis is typically considered when kidney function falls below 15 mL/min/1.73 m² (Stage 5).
Stage 1 CKD
eGFR 90 or higher and kidney damage
(e.g. uACR 30 or higher) for 3 months or more
Stage 2 CKD
eGFR 60-89 and kidney damage
(e.g. uACR 30 or higher) for 3 months or more
Stage 3a CKD
Mild to moderate loss of kidney function
(eGFR 45-59 for 3 months or more)
Stage 3b CKD
Moderate to severe loss of kidney function
(eGFR 30-44 for 3 months or more)
Stage 4 CKD
Severe loss of kidney function
(eGFR 15-29 for 3 months or more)
Stage 5 CKD
Kidney failure (eGFR less than 15 for 3 months or more) or you are on dialysis
National Kidney Foundation. (2023, September 11). Stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Early detection saves lives.
If you or a loved one are experiencing these symptoms, schedule a kidney health checkup today.
Stay ahead
Why Is Early Detection Important?
Kidney disease is progressive, but early intervention can slow its progression and prevent complications. Lifestyle changes, medication, and proper medical care can help protect kidney function for years to come.
Diagnosis of CKD
To diagnose CKD, healthcare professionals may perform:
- Blood Tests: Assess levels of waste products like creatinine and urea.
- Urine Tests: Check for protein or blood, indicating kidney damage.
- Imaging Tests: Such as ultrasounds to visualize kidney structure.
- Biopsy: Removing a small tissue sample for analysis.
Treatment Options
While there’s no cure for CKD, treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a kidney-friendly diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking.
- Medications: To control blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels.
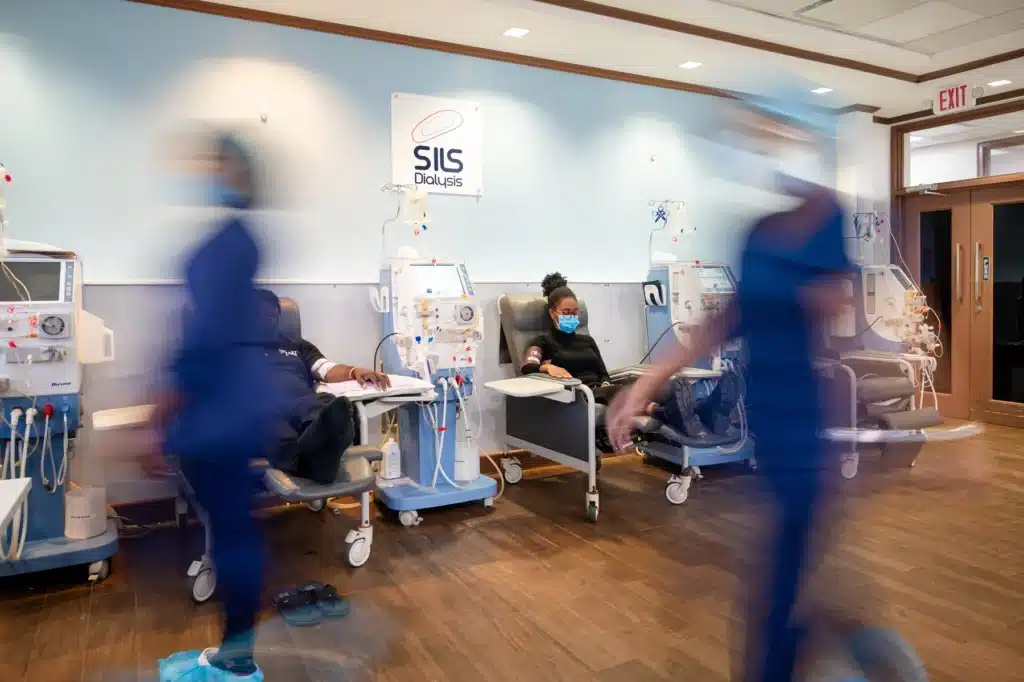
- Dialysis A treatment that filters waste and excess fluids when kidneys fail.
- Kidney Transplant: Replacing the diseased kidney with a healthy donor kidney.
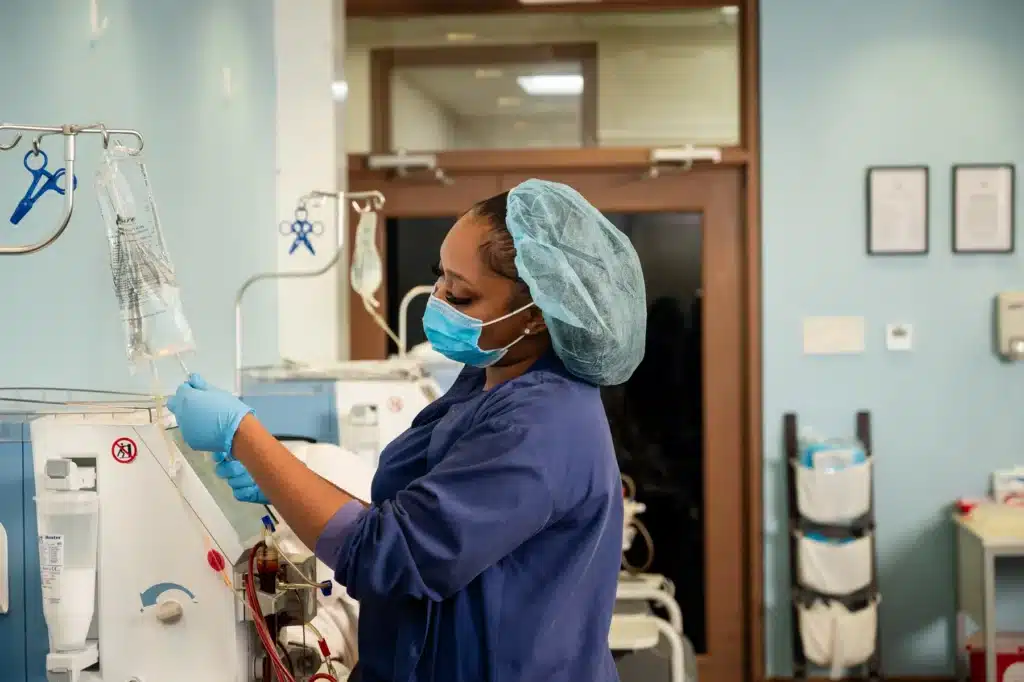
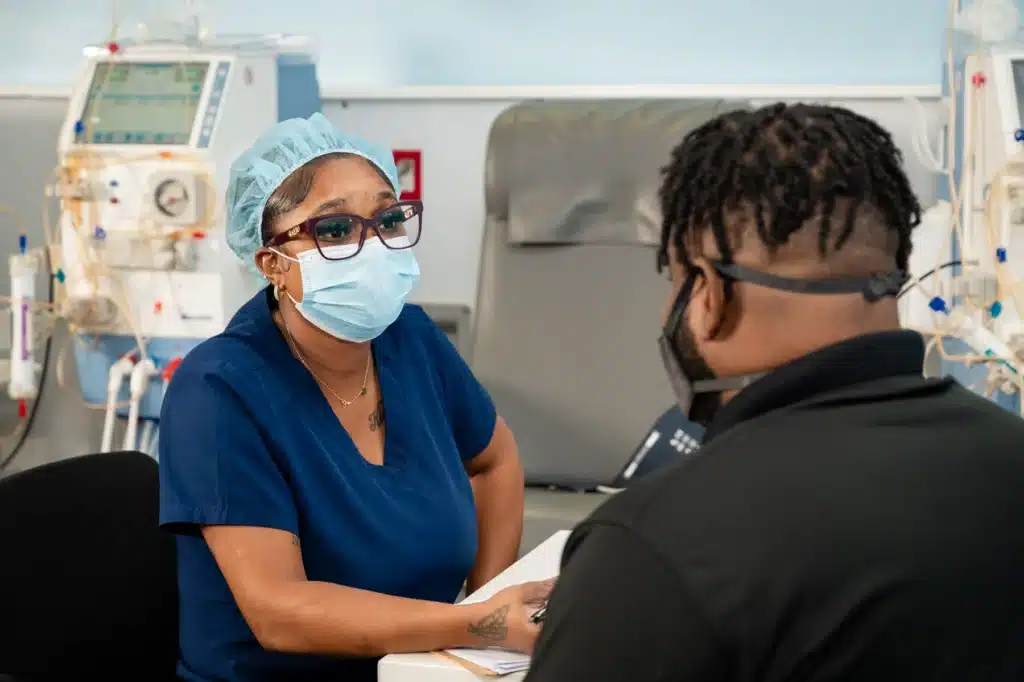
Preventive Measures
To reduce the risk of developing CKD – Maintain a Healthy Diet:
Low in salt, sugar, and saturated fats.
- Regular Exercise: Helps control weight and blood pressure.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake supports kidney function.
- Avoid Overuse of NSAIDs: Such as ibuprofen, which can harm kidneys.
- Regular Check-ups: Especially if you have risk factors like diabetes or hypertension.
Understanding CKD is crucial for early detection and management, potentially slowing its progression and maintaining a better quality of life.
